Cognitive Behavioural Therapy (CBT) for Alcohol Use Disorder in Hyderabad
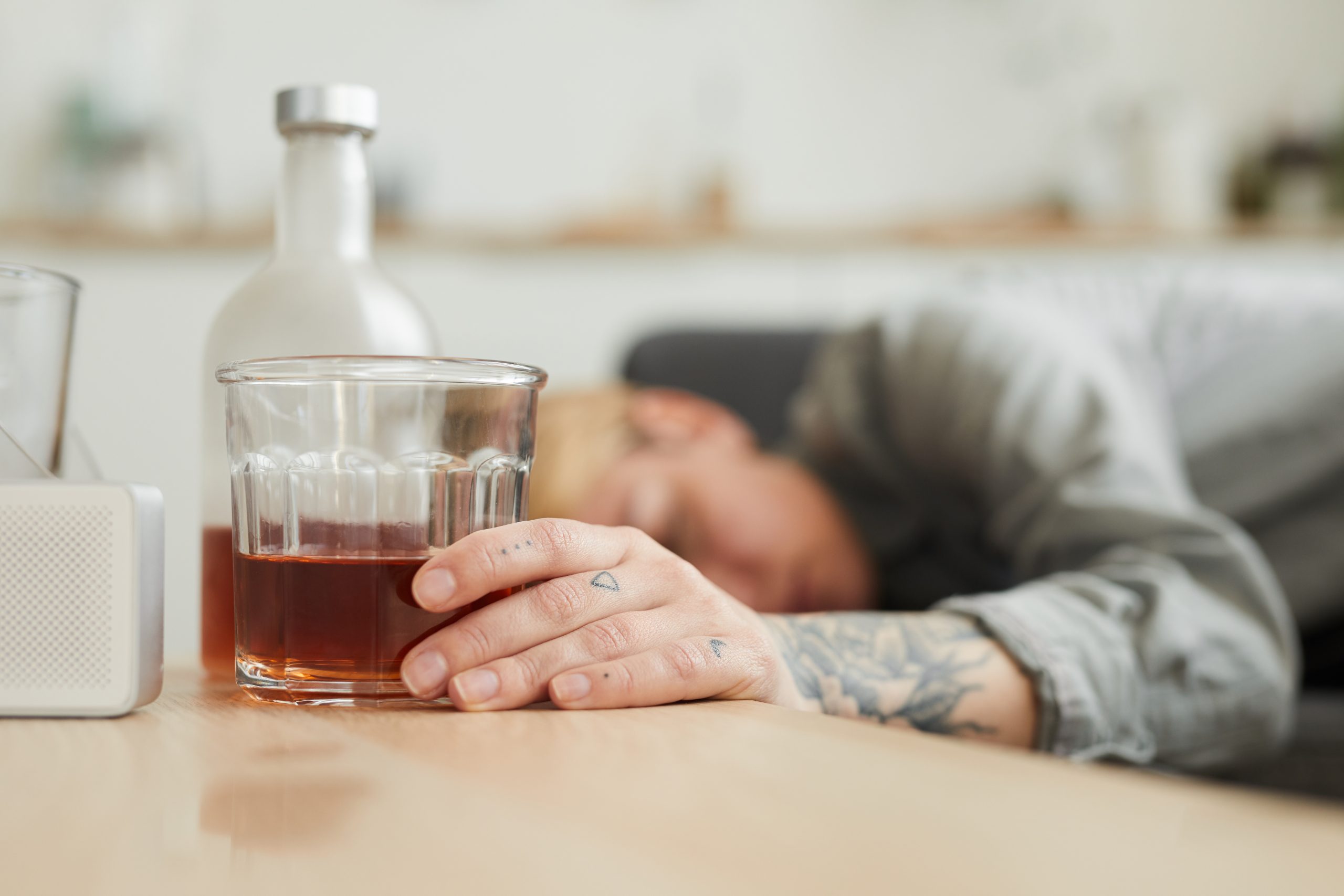
Cognitive Behavioural Therapy (CBT) is a psychotherapy that is valuable in treating alcohol addiction. The core premise of CBT is identifying and changing dysfunctional thought patterns, feelings, and behaviours, moreover, in treating alcohol addiction, CBT helps identify the negative self-defeating thought patterns that contribute to a person’s substance use. CBT uses the same learning processes that lead a person to become addicted in the first place, and teaches them to unlearn these maladaptive patterns. The primary goal in CBT is that the person learns to manage painful emotions, improves motivation, change old habits, and learns new coping skills. We offer CBT for alcohol addiction in Hyderabad. We have well-qualified and well-experienced therapists that help get to the underlying causes that contribute to a person’s addiction and make a collaborative plan with the client to overcome them and sustain recovery.
28+ Years Professional Experience
4.5 564 Google reviews
Cadabam's Hospitals
No.280, 15th Cross,5th Phase,
JP Nagar,Bangalore-560 078,India
Cadabam's Hospitals
90,Padmashree Gardens,Gowlidoddi,
Gachibowli,Hyderabad,
Telangana 500075, India
Get In Touch!
At Cadabam's, we've always got your back.
What People Say

Very happy with the facilities provided here. We are extremely grateful to Dr Vishal for his treatment and guidance. I liked the fact that he is very mindful of side-effects while prescribing medicines. Very good doctor and a very good hospital. Highly recommend.
Nithin Gopinath

Though we landed at wee hours of the night, doctors attended in time and we received professional treatment by all including hospital staff.

Excellent hospital and excellent doctors. They listen to you very patiently, do a thorough ore check before starting the treatment which inspires a lot of confidence. Dr. Madhukar is one of the best doctors I’ve met so far.
Narasimha Prasad

Very good cleanliness, disciplined, well behaved, good patience while handeling patient & their relations, good service overall excellent environment.

A good hospital for any kind of psychiatric problems. Very good and courteous staffs and well known doctors.
Anant Modi

Coordinated well I am very satisfied, very good, spent quality time with doctors & further treatment.

I visit Cadabam along with my wife to consult Dr. V. Khasi. We found the Staff very professional and polite with patients. We recommend Cadabam for anyone who requests us for the services available at Cadabam.
Sudarsan Barakman

I visit Cadabam along with my wife to consult Dr. V. Khasi. We found the Staff very professional and polite with patients. We recommend Cadabam for anyone who requests us for the services available at Cadabam.

Coordinated well I am very satisfied, very good, spent quality time with doctors & further treatment.

A good hospital for any kind of psychiatric problems. Very good and courteous staffs and well known doctors.
Anant Modi

Very good cleanliness, disciplined, well behaved, good patience while handeling patient & their relations, good service overall excellent environment.

Excellent hospital and excellent doctors. They listen to you very patiently, do a thorough ore check before starting the treatment which inspires a lot of confidence. Dr. Madhukar is one of the best doctors I’ve met so far.
Narasimha Prasad

Though we landed at wee hours of the night, doctors attended in time and we received professional treatment by all including hospital staff.

Very happy with the facilities provided here. We are extremely grateful to Dr Vishal for his treatment and guidance. I liked the fact that he is very mindful of side-effects while prescribing medicines. Very good doctor and a very good hospital. Highly recommend.
 Available
Available